Products & Services Industry Guides

Linear bearings are crucial components used in a wide range of applications, from industrial machinery to consumer products. Selecting the right linear bearing is vital to ensure smooth and reliable operation, as well as to maximise the overall performance and longevity of the system. This article explores five key factors that should be carefully considered when choosing the most suitable linear bearings for your application.
Bearings are of utmost importance in various industrial devices and equipment. Although bearing failure cannot be completely avoided, its adverse effects on company operations can be reduced. The crucial aspect lies in comprehending the factors that lead to bearing failure and implementing preventive measures to avoid premature failure.

Selecting the right linear bearing is a crucial step in ensuring the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of any system that relies on linear motion. By carefully evaluating factors such as load capacity, operation speed, precision, environmental conditions, and life span, engineers and technicians can make informed decisions to meet the specific demands of their applications. A well-chosen linear bearing can lead to improved performance, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced overall productivity. Now let’s explore the main factors to consider before you select your linear bearings.

Incorrect sizing stands as one of the primary culprits behind bearing failure. It is imperative to ensure that the bearing is accurately sized and possesses the appropriate load capacity for the specific machine. This way, the likelihood of bearing failure can be minimised, and the machine's optimal performance can be sustained.

The operational speed is another critical factor that influences the selection of linear bearings. It refers to how fast the bearing and the system it supports will be moving during operation. Higher speeds can generate increased friction and heat, which can lead to accelerated wear and reduced bearing life. Manufacturers provide speed ratings for their linear bearings, and it is essential to choose a bearing that is rated for the specific operating speed of your application.
For applications that demand accurate motion control, precision becomes a significant consideration. Precision linear bearings are designed to minimise play and backlash, ensuring precise and repeatable motion which resembles the function of linear guides in the linear motion system as well. Industries like semiconductor manufacturing, medical equipment, and optics rely on precision bearings to maintain tight tolerances and achieve excellent positional accuracy. Assessing the required level of precision in your application will guide you in selecting the appropriate linear bearing type.

The operating environment can have a significant impact on the performance and lifespan of linear bearings. Factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, dust, and chemical exposure can adversely affect bearing performance. In harsh environments, specialised coatings or sealing solutions may be necessary to protect the bearing from contaminants and corrosion. Always choose a linear bearing that is specifically designed to withstand the environmental conditions present in your application.

The lifespan of a linear bearing is an essential consideration, especially in applications where frequent maintenance or replacement is impractical or costly. Bearing manufacturers typically provide the predicted service life for their products based on specific conditions, load, and speed ratings. It is crucial to select a linear bearing with a life span that aligns with the operational requirements of your system, ensuring extended service intervals and minimising downtime.
Linear bearings are typically made from materials like aluminium and steel. It come in various types, each designed to suit specific application purposes. Understanding the different types and their suitability can help engineers and designers choose the most appropriate option for their specific needs. Here are some common types of linear bearings and their applications.
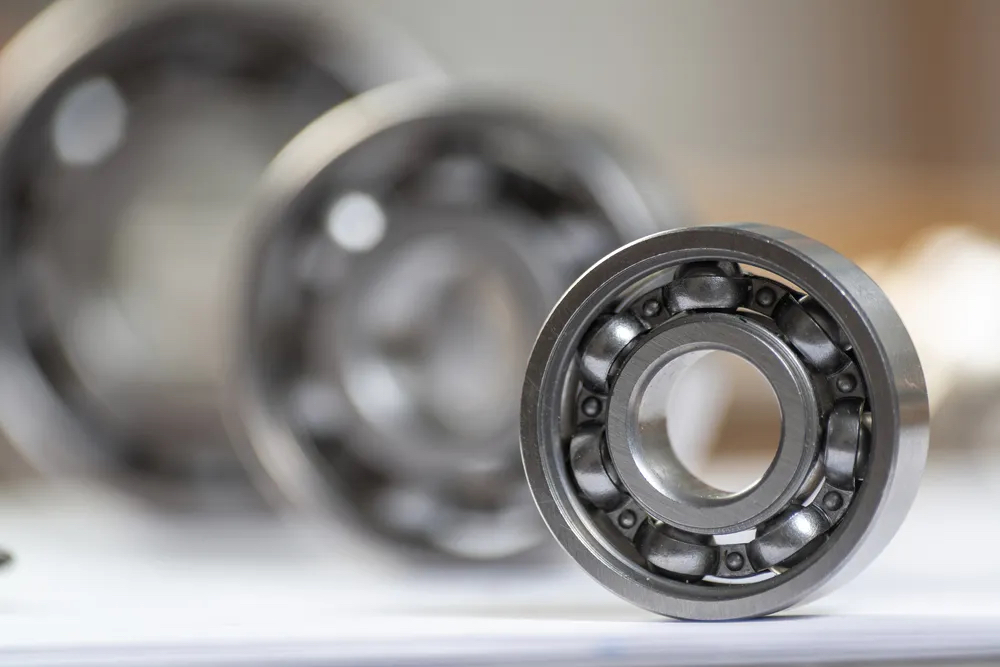

Linear ball bearings also commonly known as linear ball bushing offer the lowest friction linear movement out of all types. There are two main categories worth emphasising, linear ball bearing & linear guides. Traditional linear ball bearings are designed to be used with hardened and ground axles. These ball bearings contained small point contact areas for exceptionally low rolling friction. However, the small contact area also means they exert significant force on the axle, making it crucial to use them exclusively with hardened axles.
Linear Ball Bearing Advantages:
Low Friction & Low Noise
Extensive Range of Application
High Load Capacities & Long Lifespan
Easy Lubrication, both oil & grease can be applied.
Suitable for general-purpose linear motion applications with low friction requirements. Applications can include CNC machines, 3D printers, automation equipment, and robotics.
Linear guides are also linear ball bearings except that they operate on a profiled rail. The rails of linear guide typically has a ball groove shaped like a gothic arch to maximise load-carrying capacity. The rail's strength is essential to prevent the balls from deforming it, ensuring precise linear movement.
Linear Guide Advantages:
Lubrication & Maintenance Free
Hygienic, Corrosion & Wear Resistance
Up to 40% more economical than the traditional linear ball bushing
Suitable for high-precision and heavy-duty linear motion applications. Applications can include CNC routers, machine tools, and precision measuring instruments.
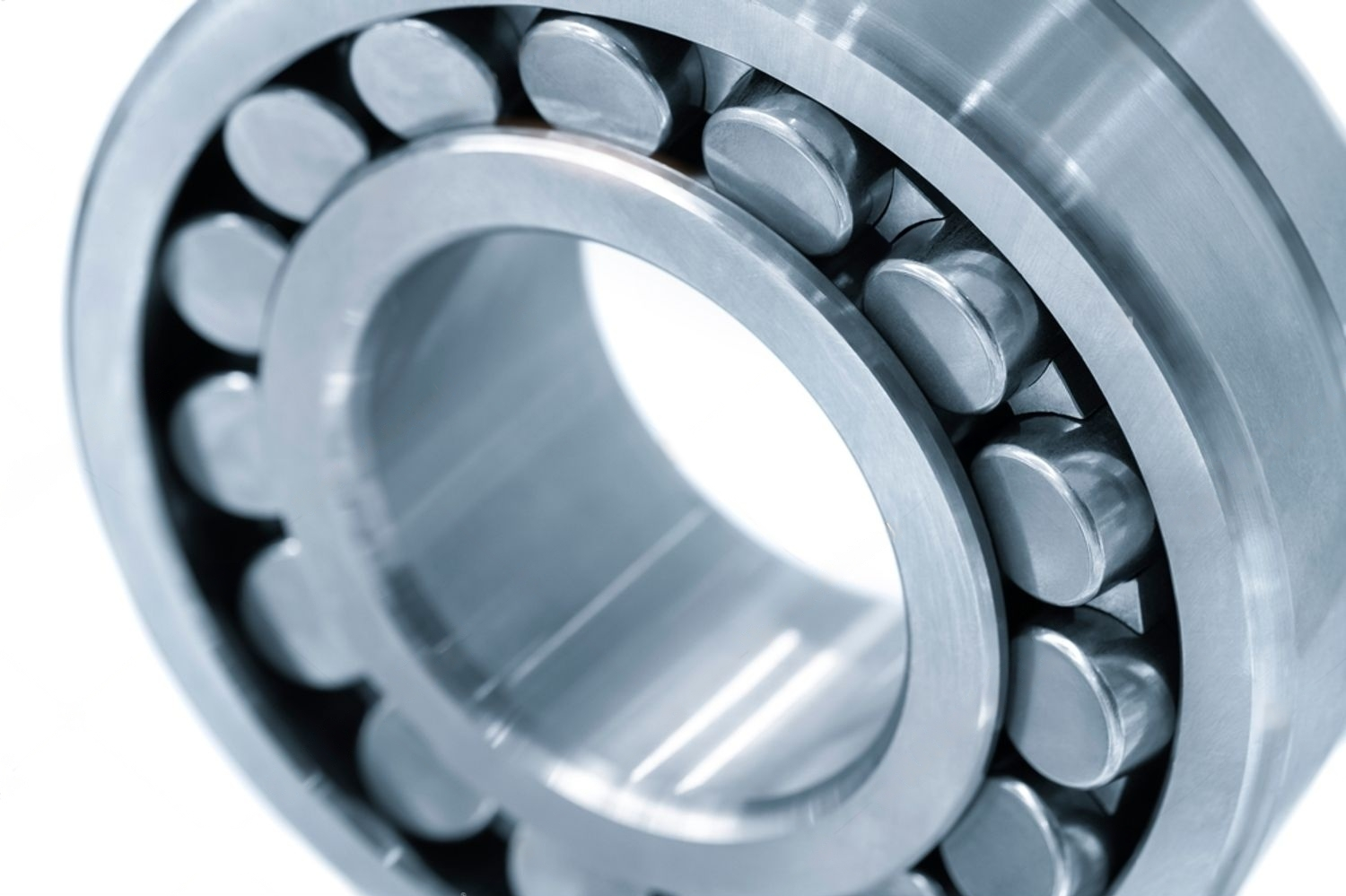

These bearings are the most common type of bearings and includes, roller chain, roller guides, cross roller linear slide, and plain bearings. Roller bearings offer a higher basic load rating compared to ball bearings of the same size. Nevertheless, they are less tolerant of lateral forces.
Main Advantages:
High Load Capacity & Durability
Ability to withstand Momentary Shock Loads
Accuracy of Shaft Alignment
High Rigidity
Suitable for heavy-load linear motion applications. Applications can include industrial machinery, material handling systems, and conveyor belts.
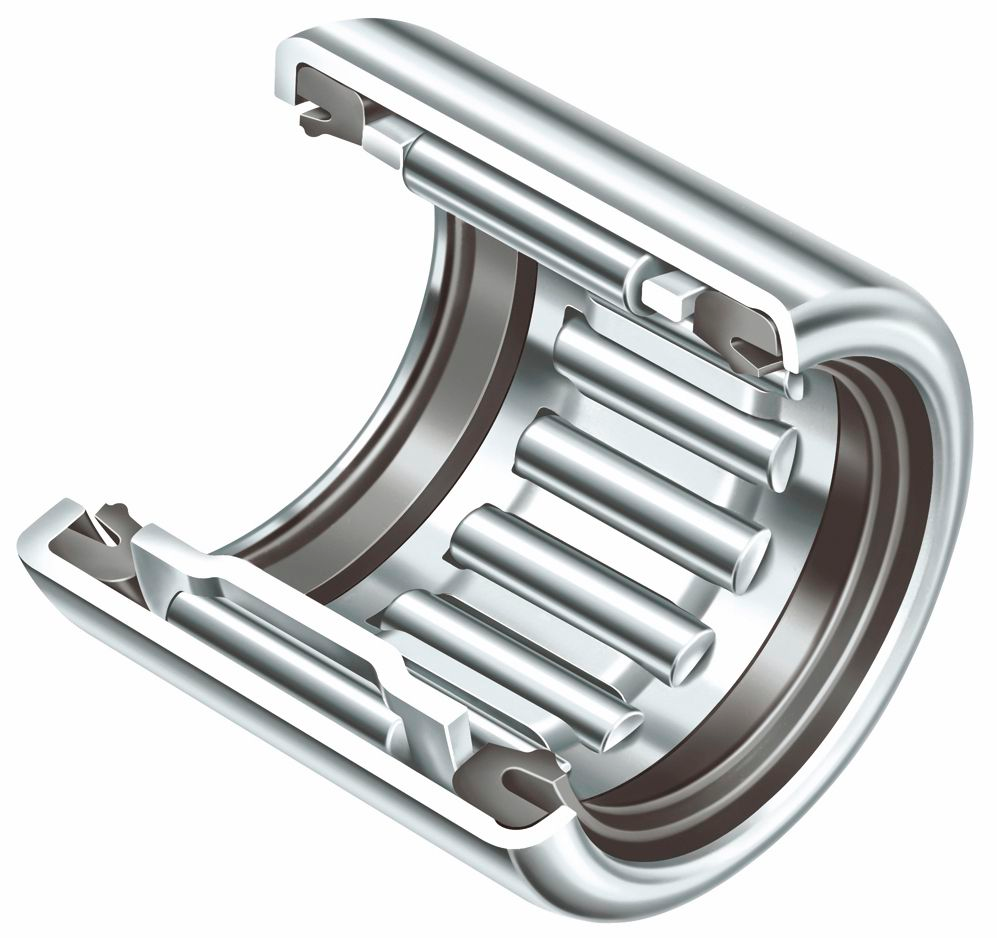

This type of bearing utilises small, cylindrical rollers to reduce the friction between moving components and help support heavy loads. These type of bearings have a large load-bearing surface to nearly 4 times compared to regular rolling bearings, providing exceptional load capacity and stiffness. They are usually designed to accommodate axial-oriented forces more then 5% of the radial load and will need some type of lubricant to help dissipate heat and reduce friction.
Main Advantages:
Compact Design
High Load-Carrying Capacity due to Greater Surface Area
Relatively Low Maintenance
Suitable for applications with limited mounting space and high radial loads. Applications can include automotive, machine tool spindles, and aerospace equipment.
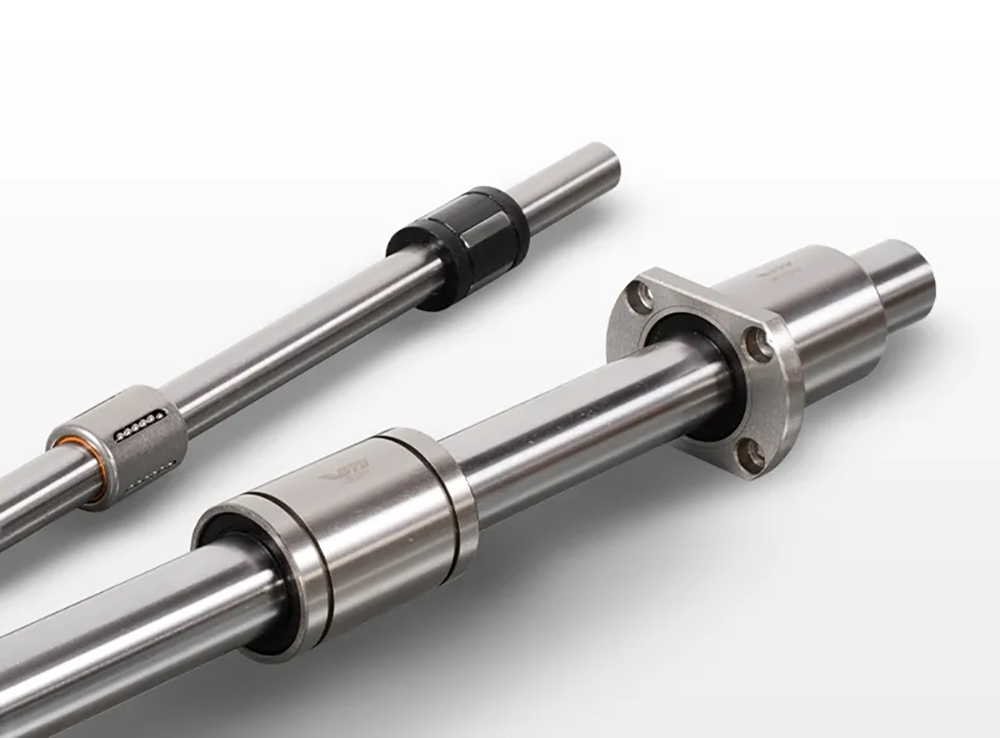

Round shaft linear bearings are used in many mechanical systems that require precise and smooth linear motion. These bearings are designed to enable smooth movement along a straight path, it consists of an outer cylinder or sleeve and rolling elements, typically balls or rollers, placed between the shaft and the sleeve. This arrangement allows for efficient transfer of loads and minimises friction, ensuring consistent and reliable motion.
Main Advantages:
Exceptional Accuracy & Repeatability
Easy Installation
Consistent & Reliable
Suitable for low-cost and low-friction linear motion applications. Applications can include manufacturing, robotics, linear actuators, transportation, and packaging equipment.
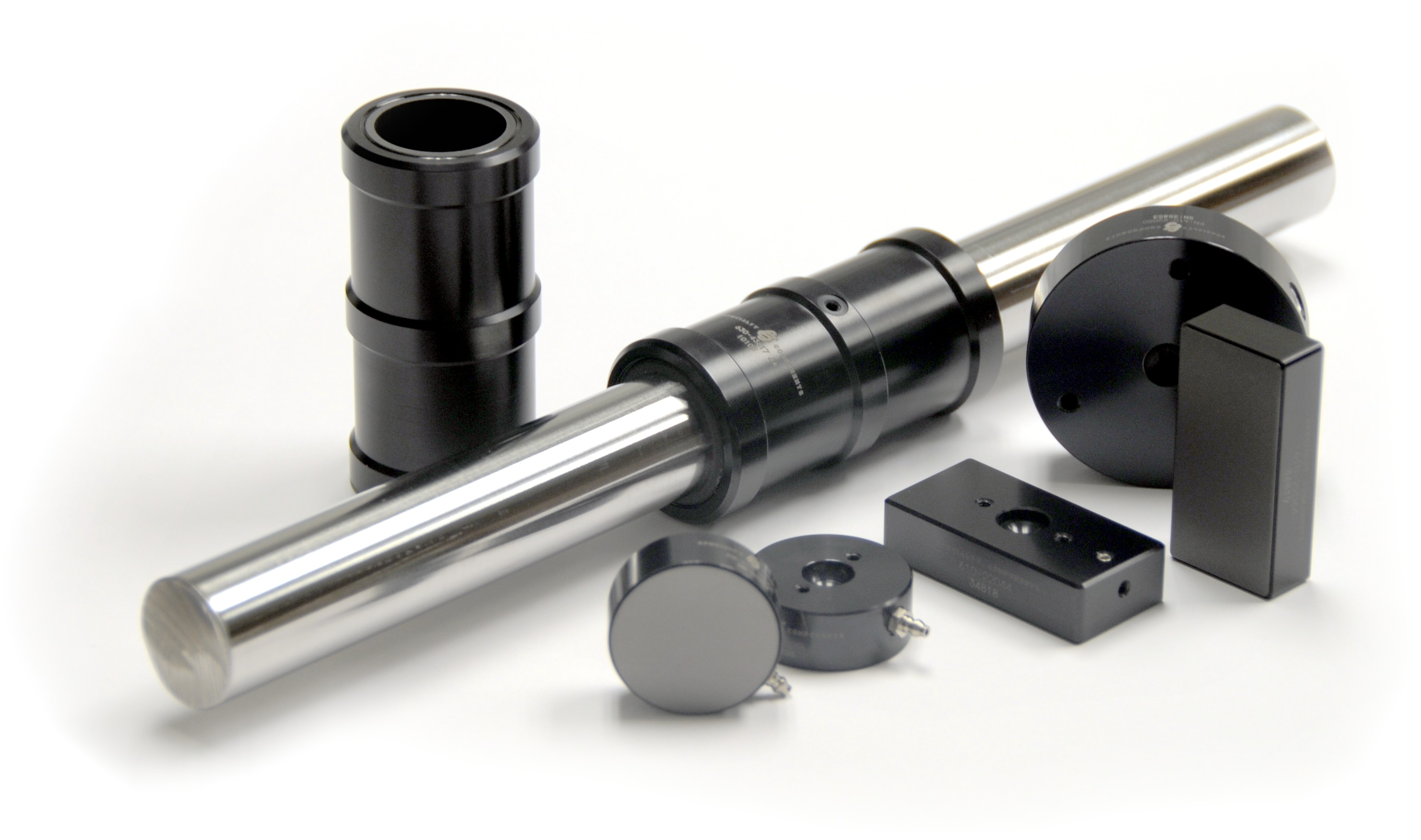

Linear air bearings are cutting-edge technology in the field of linear motion and precision engineering. These innovative bearings utilise a thin cushion of air to create a frictionless and smooth movement along a linear path. Unlike traditional mechanical bearings, which rely on physical contact between surfaces, linear air bearings provide virtually no contact and offer significant advantages in terms of accuracy, precision, and speed.
Main Advantages:
Zero Friction
High Precision
Vibration-free Operation
Suitable for ultra-high precision and frictionless linear motion applications. Applications can include semiconductor lithography, optical inspection, laser engraving systems, and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs).
Each type of linear bearing has its strengths and limitations, and selecting the right one depends on factors such as load capacity, precision requirements, operating environment, and budget constraints. By carefully evaluating the specific needs of their application, engineers can make informed decisions and avoid making mistakes involving their linear bearings that might be costly afterwards.
In this comprehensive article, we provided practical tips for assessing factors like load capacity, operation speed, environmental factors, which impacts your selection process. Through in-depth research and expert insights, we hope you have gain the knowledge and insights required to make informed decisions to ultimately lead to enhanced performance and efficiency in your linear motion systems by using the right linear bearings for your systems.

 联系我们
联系我们 