Products & Services Industry Guides
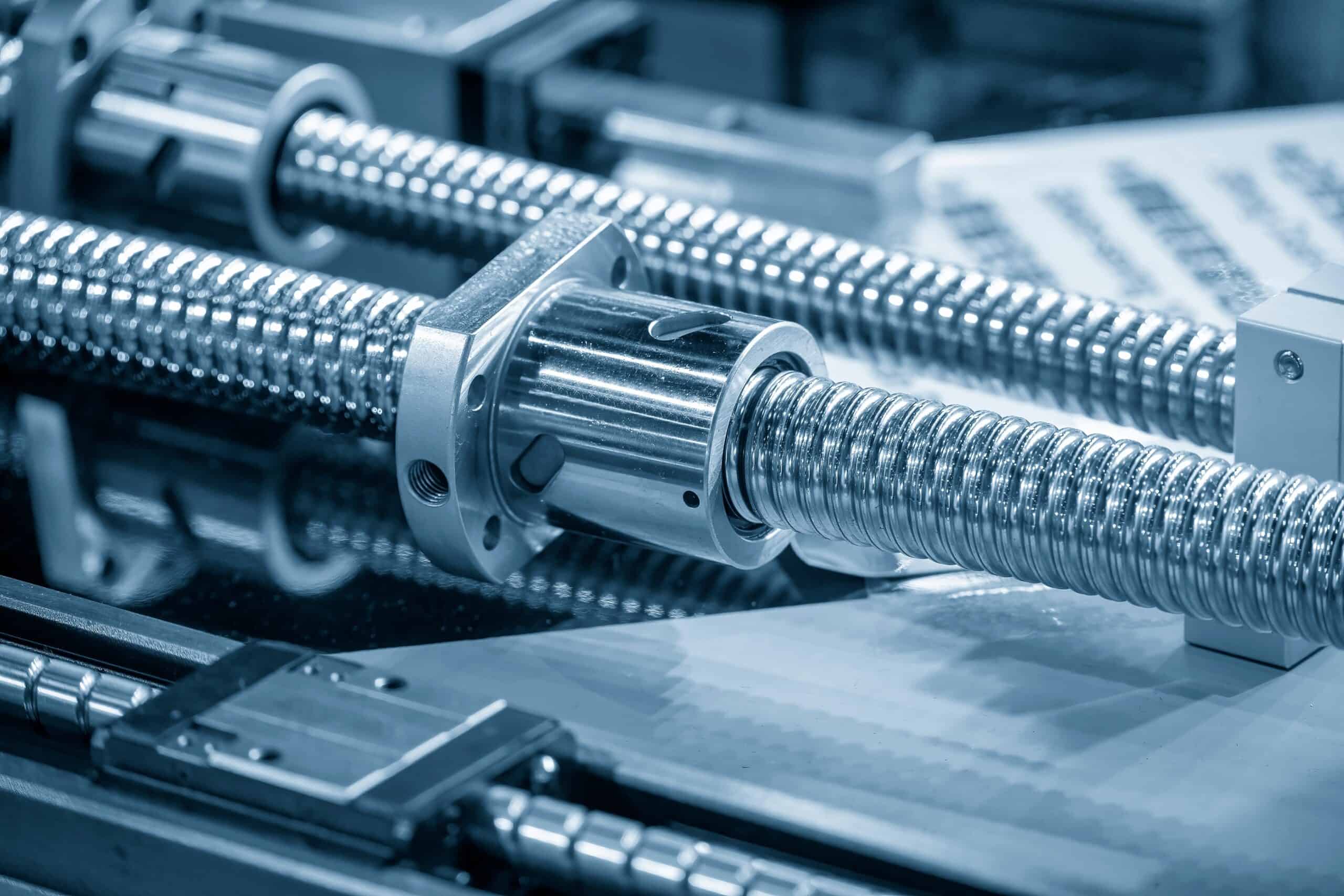
Linear motion guides are essential components in mechanical engineering in various sectors, such as the medical equipment and semiconductor manufacturing equipment industry. Utilising bearings developed for rotary movement, linear motion systems are created to circulate high-load capacity in a straight line easily.
The key feature of this machine is its ability to convert rotary movement into linear motion with a stroke of high precision. This is made possible by the rolling elements or bearings, which glide along a predetermined linear rail to allow a smooth and controlled motion.
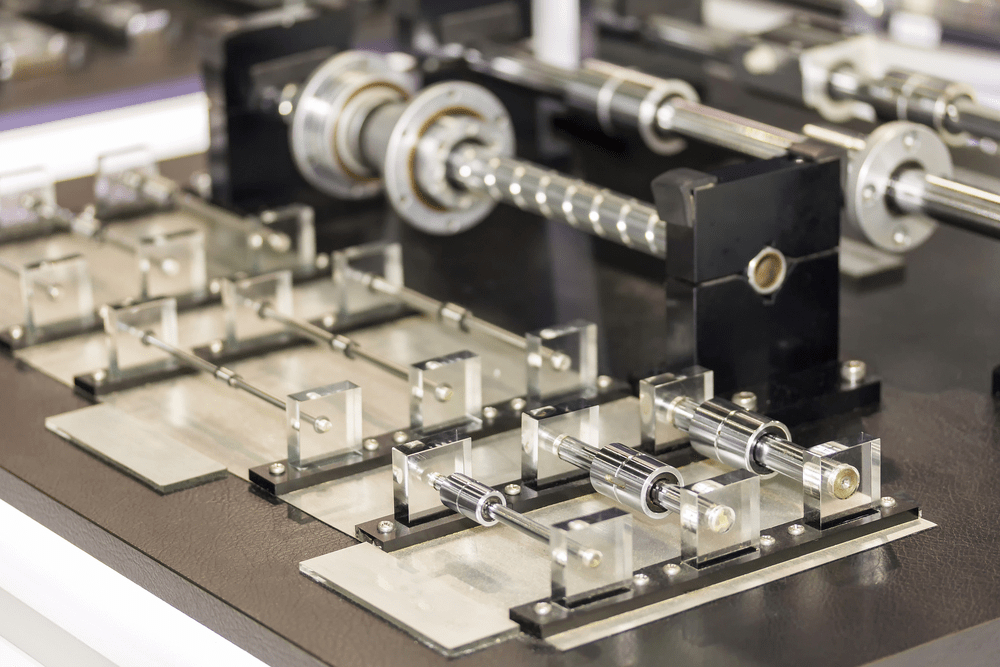
A linear motion system is often referred to as a linear guide, and it comes in different types and configurations, including ball guides, roller guides and numerous miniature guides, among others, to cater to specific application requirements. Although the design might differ, the linear guide maintains its high rigidity and capability to move high loads across its selection.
These guides can be used in diverse applications, including CNC machining, 3D printing, and household necessities like drawers and sliding doors. As technologies and machinery continue to advance, so does the increased need for linear guides.
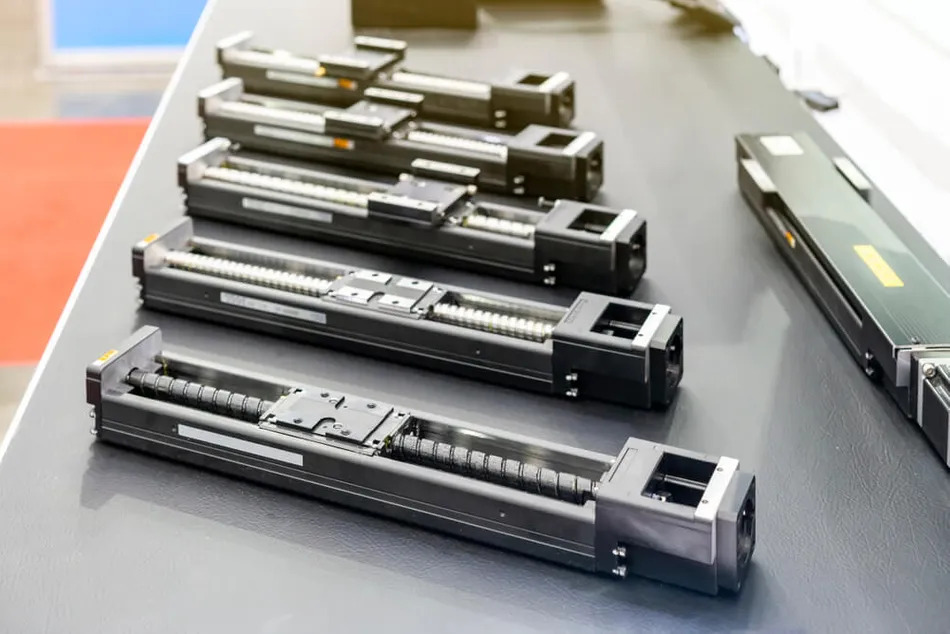

Linear guides provide a controlled and low-friction mechanism for heavy loads or objects to move straightly with high precision. The mechanism involves rolling balls as recirculating elements between rails and blocks, greatly enhancing the machinery's motion. Below is how linear guides work to assist machine tools.

The linear guide features two main components: stationary linear rails and movable carriage, typically known as a slider. The rails serve as a mounting point, providing a linear path for the load. At the same time, the carriage is attached to the gear that needs to move linearly.
Some standard rail configurations are round rail, profile rail, crossed roller rail, flat rail, and custom rail.

Designed to reduce the friction between rail and carriage, the linear guide has ball screws or circular rollers as a recirculating element that reduce the contact surface area along the rail length. This resembles a round shaft linear motion system that produces smooth movement and minimal resistance between the carriage and the rail. The mechanism allows for a rolling motion rather than a sliding contact.
Linear guides are engineered with a structure to support and carry loads in a precise direction. They can handle axial, radial, and even torque forces. The load capacity of linear guide rails mainly depends on the size range and the number of environmental conditions.
In addition, the load will be distributed evenly across the tracks and rolling elements. Ensuring the load is spread out helps reduce the concentrated weight stress and the risk of premature bearing failure.

The repetitive moving component in machine tools makes having precise positioning indispensable. This makes linear guideways a suitable match for such operation since it has low friction, high rigidity and accuracy needed. These features ensure a minimal deviation from the predetermined path for the carried load.

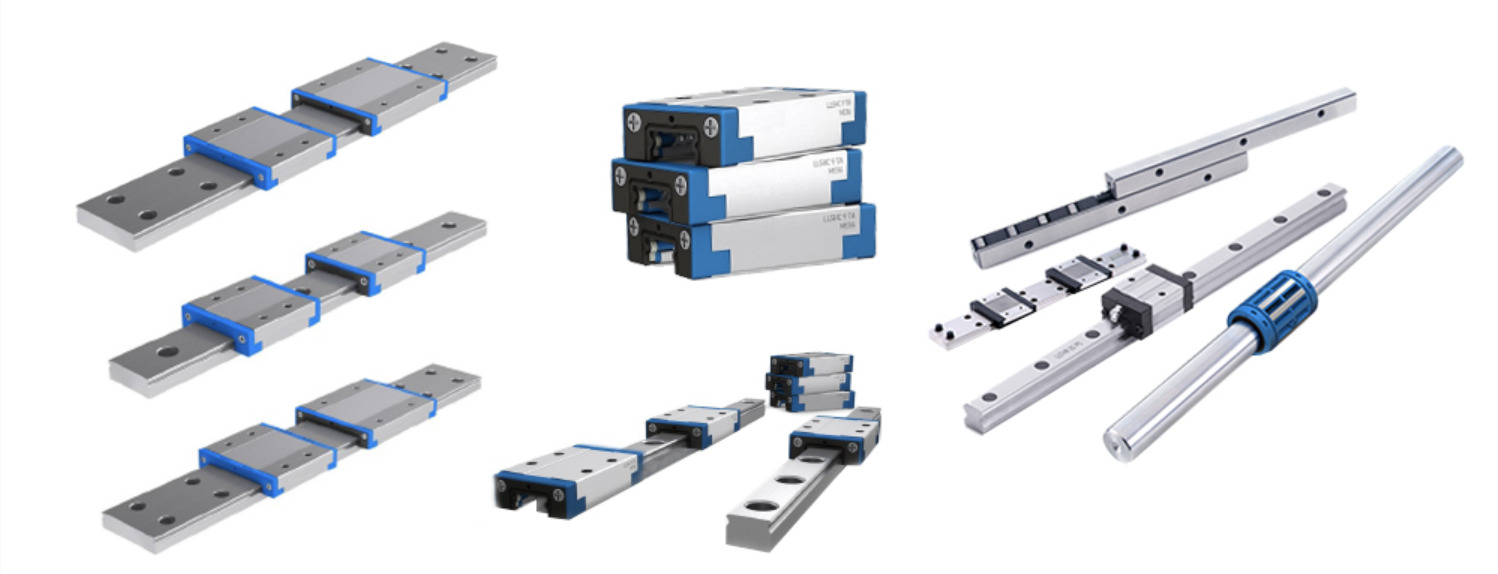
Linear guide rails or linear guideway is crucial for different types of machinery. It has several key features that help provide a stable platform for linear motion with such high accuracy. The key components and accessories include rail, carriage, and rolling elements.
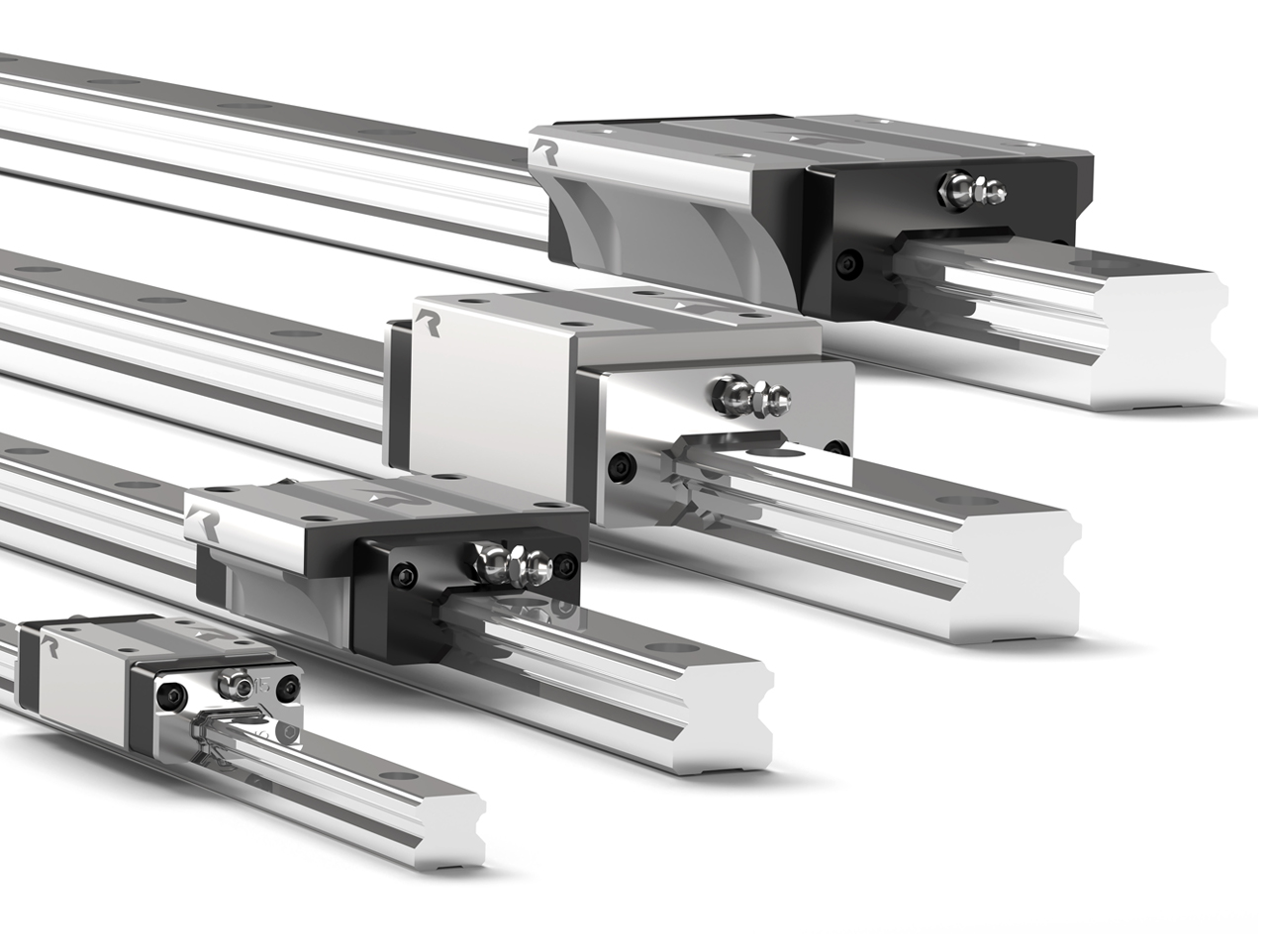

The main structural component of the linear guide rails is the rail or track. This machine part is typically made of stainless steel or aluminium, chosen for its robust faculty to maintain rigidity and provide durability. The rail features various profiles, such as square, round, and rectangular, to suit and accommodate different weights and applications. The rail length may also differ to meet the desired travel distance.
The moving components of the linear guide rails and systems are called carriages, which glide along the linear guide rails. The carriage is used as a housing space for rolling elements as well as a mounting platform for the loads to be moved. They are designed to carry a wide range of weight evenly, depending on the specific application and requirements.
The carriage also has different configurations, such as blocks or flange-style, that can be chosen according to the suitable application, and some even incorporate dust seals or wipers to protect the rails from dust and contaminants.
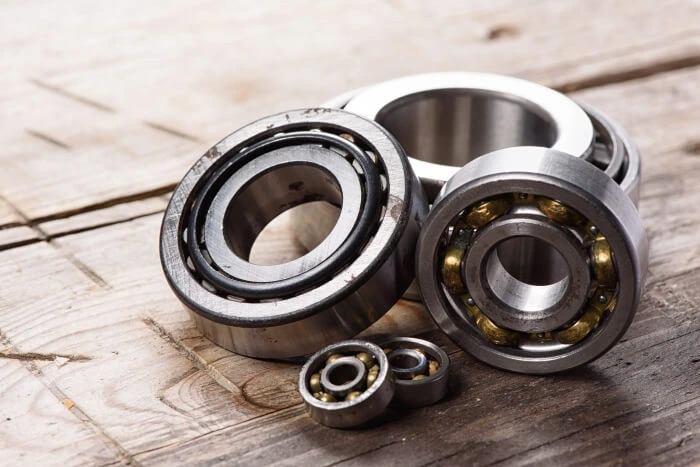

To reduce the contact area and ensure smooth movement between carriage and rail, the recirculating rolling elements are incorporated into linear guides, minimising friction and wear. There are a few types of rolling elements used in linear guides, which include :
These compact small steel balls are housed between the carriage surfaces and rail. These types of bearings are suitable for high-speed, low and moderate-weight applications.
Unlike balls, the rolling elements of roller bearings consist of tapered or cylindrical rollers for handling more loads and heavy-duty applications. It is also more well-suited where radial loads are the primary concern of the applications.
Suitable for small space and high radial load requirements, these compact needle bearings' rolling elements are made with cylindrical rollers resembling tiny needles. This structure is made for load with a high length-to-diameter ratio.
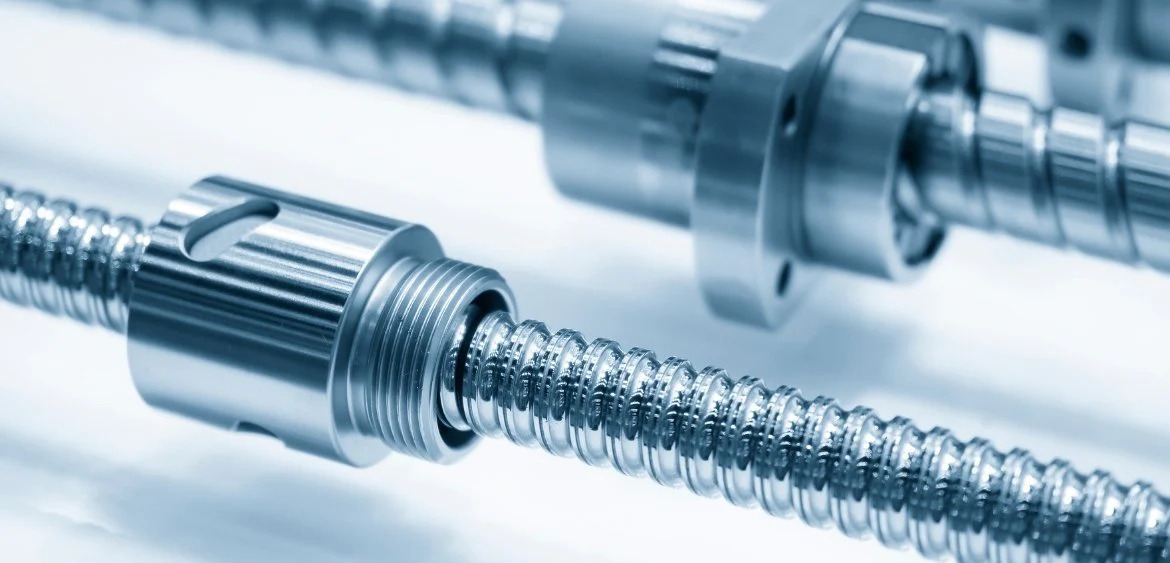
Several linear rail guides are available designed to fulfil specific requirements. Some are made of stainless steel, aluminium and other choice of materials. This mainly depends on the environmental condition, mounting requirement and the specific application. Here are some of the common types of linear guides and their typical application:
Profile rail guides are made of precision-ground rails and ball-bearing or roller-bearing carriages. They are the actuators for applications requiring high-stiffness, precision and substantial weight capability.
This model is mainly used in high-speed machining centres, aerospace systems and robotics fields.
Ball bearings linear guides are commonly used in various industries due to their versatility. These ball guides fit those searching for exact guides with smooth, low-friction motion.
The applications of this model of bearings are quite robust, ranging from 3D printers, medical devices, CNC machines and transportation systems.
Roller bearings are often used for heavy-duty applications and higher weight capacities, as they possess more weight capacities than ball-bearing guides. Large machine tools, automation equipment and material handling systems are some industries where this model can be utilised.
Characterised by their compact design and high radial weight capacity, needle rollers find use in limited space. Due to its thin and long design, it is a solution for small linear stages, positioning tables and precision instruments.
Similar to Needle Roller Guides, Slide Guides are often utilised where space is finite and the environment calls for high precision. There are various applications for these compact miniature guides, including electronic equipment, optical instruments and small-scale positioning systems.

Linear guides play a pivotal role in facilitating precise linear motion, and selecting the right one can significantly impact the performance and longevity of your equipment as well. Therefore, it is vital to take the time to understand and make an informed decision to ensure your machines operate seamlessly.
At SLS Bearings, our experts in technical support help you choose the right linear guides and find bearings for your specific application. If you need assistance with further information or are ready to place an order, our dedicated team is just a click away.
Contact us today to learn more about our linear guides and how they can bring value to your business.

 联系我们
联系我们 